The concept of matter, energy, element and atom are significantly important in chemistry, especially in Branches of Organic Chemistry. Matter consists of basic elements which has specific physical and chemical properties. While element consists of one atom type. Atom is the smallest particle in the element. Even though it’s considered as smallest part of an element, atom is not really the smallest part in element or matter.
Atom can be divided into smaller particles consisting of proton, electron, neutron. The basic concept of these theories is really vital to understand the chemistry as a whole study. This article will cover the basic concept of atom (proton, electron, neutron) and its application in chemistry.
Basic Concept of Atom: Proton, Electron, Neutron
As we mentioned previously, atom is the basic part of matter. Atom defines the chemical and physical properties of an element. In general, atom consists of 3 particles which are proton, electron, neutron. The structure of atom consists of 2 main parts which as nucleus and electrons. Nucleus is the mass center of an atom.
However, it has less volume compared to the electrons. In nucleus, we can find the proton and neutron. In term of mass, proton and neutron has larger mass than the electrons. Proton and neutron is located on the center of atom. This is where the nucleus lies. While electrons are really light. They exist in the cloud which orbits the nucleus, the center mass of an atom. In contrast, the radius of electron cloud is higher than the radius of nucleus. Electron cloud has the 10.000 times larger radius than the nucleus.
Structures of Atom
As it said, the atom structures consist of two main parts which are nucleus and electrons. Thus, here are the explanation of nucleus and electrons:
- Nucleus Concept
As mentioned before, nucleus is the center mass of the atom. Scientists successfully discovered this part in 1911. It’s the work of Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden who work under Ernest Rutherford. They did bombarding the metal foil using alpha particles. The intention was to identify how they scattered. Firstly, they thought that the alpha particles would pass though the atom in the straight path. This was based on the previous study from J.J Thomson. Thomson said that the atom charges are really diffuse as the electric field would not influence the alpha particle.
However, based on their experiment, the alpha particles were deflected with the angle greater than 90 degree. Based on this, Rutherford came up with the theory that there were positive charge of atom in its center. This center of atom is then called as nucleus. Even though it has the tiny size, this part has the largest mass in atom. This nucleus part consists of proton and neutron.
- Discovery of Electron
J.J Thomson was the first man who discovered the electron. He measured the cathode ray mass and found out that the cathode ray consisted of many tiny particles. The measurement showed that these particles had very light mass c ompared to hydrogen atom. Electron was the first subatomic particle which was discovered by scientist. J.J Thomson also succeed to discover the particle which carries electricity in the metal wire and carries negatively charged part in the atoms. He got the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1906 for this discovery.
Particles of Atom
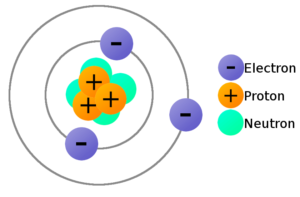 Meanwhile, atom consists of three main particles which are proton, electron, and neutron. For further explanations, here are the definition, concept, and worksheets of proton, electron, neutron:
Meanwhile, atom consists of three main particles which are proton, electron, and neutron. For further explanations, here are the definition, concept, and worksheets of proton, electron, neutron:
1. Proton Concept
Proton is the particle in the nucleus having the positive charge. This part was found by the famous scientist named Ernest Rutherford. He conducted the experiment to find out this part in 1911 till 1919. The proton amount in the atom gives the specific characteristic for certain element. Carbon atoms have six protons, while hydrogen atoms only have one proton. This number defines the chemical properties of this element.
The number of protons in one atom is called the element atomic number. The next section will detail this atomic number and atomic mass. The atomic number has strong relation with the Periodic Table of Element. This table arranges the element in this earth with the order of increasing atomic number. Proton has the mass of 1.6726 X 10-27 kg.
Thus, a scientist named Golstein did a research of proton using a tube-like Crookes. Then , the cathode made open and put down there and filled with hydrogen. The research showed there are two rays. The first cathode electron rays moved to anode. The second rays moved to cathode, an the partial rays moved to holes channel. Then, the particle is proton.
2. Electron Concept
While the protons have positive charge, electrons have the negative charge. The positive charge in the protons will attract the negative charge of electron electrically. The mass of electron is approximately 9.1095 x 10-31 kg. Its weight is much smaller than the proton or neutron. Electrons are the moving parts in the atomic structure. They do surround the nucleus in such a path which is called electron orbitals.
There are different forms between the inner and outer orbital. The inner orbital has the spherical form while the outer ones has more complicated form. The location of electrons in the orbital defines the configuration of electron. This configuration of electron will then determine the properties of atom. The properties consist of conductivity, boiling point, stability, magnetic properties and some others.
Electron has also ability to create create the chemical bond. Atoms can attach to other atoms by using the chemical bond. This bond will then create the chemical compound like molecule. In this reaction, electrons play the significant role. In chemistry study, the outermost electron shells play more important part than the inner electron shell. Both inner and outer shell of electron do define the electron configuration, but the inner orbital is often replaced by the symbol. The electron configuration will explain the electron orbital form and the number of electrons in each orbital.
3. Neutron Concept
Differs from electron and proton, neutron is the no-charge part in the atom. Meanwhile, neutron is neutral. Neutrons are in the nucleus, the center of the atom. Neutron has the mass of 1.6750 X 10-27 kg. Its mass is slightly bigger than the proton’s mass but higher than the electron’s mass.
The scientist James Chadwick is the one who successfully discovered this atomic part. He found neutron particle on his experiment in the 1932. The presence of other particles in the uncharged nucleus of atoms was proved by Chadwick. He did a research by shooting beryllium metal using alpha rays.
There was a research by Rutherford, he noted that mass of atomic nuclei is always bigger than proton on atomic. Thus, Rutherford suspects that there are other participles in the nucleus that are uncharged because the atoms are positively charged by positive proton.
Atomic Number and Mass Number
Atomic number and mass number are other useful basic information in chemistry, especially in organic chemistry. The atomic number is the amount of protons in an atom. This atomic number will determine the special characteristic, both chemically and physically, of an element.
Each element has its own unique atomic number. It means that atoms in the same element will always have same proton numbers. So, basically proton is the part which will define the behavior of an element instead of electron. However, electron will play the important part as the chemical reaction and bonding agent.
The atomic mass is the amount of protons and neutrons in the atom. It’s also often called as atomic weight. Differs from atomic number, the atoms in the same element may have the different atomic mass, even though they have same atomic number. This means that the atoms have same proton numbers but different neutron numbers. These atoms are known as isotopes.
The amount of neutron in the atomic nucleus will define the isotope of that element. The popular example of isotope is the hydrogen element. Hydrogen has three isotopes consisting of protium, deuterium and tritium. Protium has one proton, one electron and zero neutron. It’s the basic form of an hydrogen. Deuterium has one proton, one electron and one neutron. While tritium has one proton, one electron and two neutrons. We can see here that all these hydrogen atoms have same number of proton (1 proton) but different number of neutron.
Application of Proton, Electron, Neutron
The general concept of proton, electron, neutron is really important in the chemistry study. So, basically the use of proton, electron, neutron concept would be on the development of chemistry study. The basic concept of atom gives the clearer information about an element and matter that will further inspire other scientists to make research about advanced chemistry. So here’re some applications of proton, electron, neutron in our life.
You may also search:
1. Isotopes application
The concept of isotopes has been applied since many years ago by the ancient people. They made this concept to define the isotopes proportion in the mummy or fossil of human tissues. They were able to determine the age of certain fossils or artifacts by using the isotopes of radioactive. In that experiment, they could use the fossil itself or the material like rocks around the fossil.
The direct measurement to the fossil was often conducted if the fossil is still young enough. While the indirect measurement of fossil using rock was used for older fossils. Besides, isotopes also has useful application in medical use. They are the source of radiation which can be used in the medical diagnostic and treatment method.
2. Radioactive Application
The concept of isotope in atoms really gives the great contribution to the development of radioactive study. With the good understanding of isotope, scientist are conducting studies about the radioactive and its application to human life.
Scientists discovered that the highest radioactivity will occur in the most unstable condition of an isotope. Isotopes can have either stable or unstable condition. Unstable isotope means that the isotope has the big possibility to decay. When the isotope begins to decay, it will release the radioactivity.
This is why these isotopes are called radioactive isotopes. The popular example of element having the radioactive isotopes is uranium. It has the radioactive isotopes like 235U. This radioactive isotope has the application in the nuclear power. It can be the source of atomic bomb or the nuclear energy plant.
You may also search:
